lumbar foot drop but normal nerve conduction test|sensory nerve conduction test : services Foot drop is sometimes caused by a mass pushing on a nerve. This can be an overgrowth of bone in the spinal canal or a tumor or cyst pressing on the nerve in the knee or .
web13,588 loira pagando boquete FREE videos found on XVIDEOS for this search. . Safada pagando boquete gostoso 22 sec. 22 sec Cleidesilva010 - 720p. novinha pagando boquete 4 min. 4 min Brazilianguy420 - 720p. Negra pagando boquete amador 14 sec. 14 sec Gabrieldany2018 - 360p. NOVINHA PAGANDO BOQUETE PRO NOVINHO .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webFrete grátis no dia Compre Caixa De Fralda Pampers parcelado sem juros! Saiba mais sobre nossas incríveis ofertas e promoções em milhões de produtos. . Fralda Pampers Premium Care Pants Xxg Com 60 Unidades Gênero Sem Gênero. por Drogal Farmaceutica. Avaliação 4.8 de 5. 252 opiniões. 4.8 (252) R$ 116, 24. em. 12x . R$ 11, 30. Frete .
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common neurologic problems encountered by family physicians. 1, 2 Peripheral neuropathy can be classified clinically by the .A nerve conduction study is a test that can help diagnose issues with your peripheral nerves, such as peripheral neuropathy and nerve compression syndromes. Healthcare providers often .
RESULTS: Clinical examination and electromyography (EMG) disclosed 20 peroneal nerve lesions, nine cases of L5 radiculopathy, and 11 nerve lesions extending .Purpose of Nerve Conduction Studies. Make diagnosis of nerve injury. Identify pattern of nerve conduction studies that are abnormal to make diagnosis; i.e. sural, peroneal motor, and tibial . 1. Activity: Is the muscle turning on and off normally? Normal muscles turn on when necessary and turn off when they don’t need to act. An EMG test will record electrical activity when the muscle turns on. If an EMG . Foot drop is sometimes caused by a mass pushing on a nerve. This can be an overgrowth of bone in the spinal canal or a tumor or cyst pressing on the nerve in the knee or .
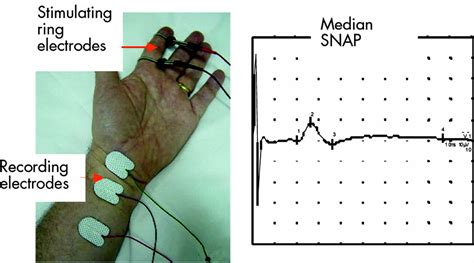
sensory nerve conduction test
Neurology Diagnosis and Screening for Neurological Conditions. What is a nerve conduction velocity test? A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test measures how fast an electrical impulse moves through your nerve. NCV can identify nerve .Foot drop is a common and distressing problem that can lead to falls and injury. Although the most frequent cause is a (common) peroneal neuropathy at the neck of the fibula, other causes include anterior horn cell disease, lumbar .A nerve conduction test, also known as a nerve conduction study (NCS) or velocity (NCV) test, uses electrical impulses to assess nerve damage. . It causes weakness of the foot and lower leg muscles. . which contains a .
hardness test specimens
The diagnosis may be confirmed with electrodiagnostic studies, including nerve conduction tests and electromyography, although the value of such testing is debated. 1 Your provider also may check for numbness on your shin and on the top of your foot and toes. Imaging tests. Foot drop is sometimes caused by a mass pushing on a nerve. This can be an overgrowth of bone in the spinal canal or a tumor or cyst pressing on the nerve in the knee or spine. . (EMG) and nerve conduction studies measure electrical .EMG and nerve conduction studies are used to help check for many kinds of muscle and nerve disorders. An EMG test helps find out if muscles are responding the right way to nerve signals. Nerve conduction studies help to check for nerve damage or disease. When EMG tests and nerve conduction studies are done together, it helps providers tell if .Another common cause of foot drop is Lumbar radiculopathy. L5 radiculopathy is the most common lumbar radiculopathy and results from lumbar disc herniation or spondylitis in the spine. . When testing the foot and ankle a positive test for foot drop is NO active dorsiflexion in a non weight bearing position. . Electromyography (EMG) / Nerve .
sensory nerve conduction study
An EMG—electromyogram—is a test that checks the health of nerves and muscles. An EMG involves inserting tiny needles into your muscles to record electrical activity. Your doctor may recommend this nerve conduction study to help diagnose nerve and muscle diseases and seizures. Read on to learn about conditions that doctors may diagnose with .a nerve conduction test (NCS), where small metal wires called electrodes are placed on your skin that release tiny electric shocks to stimulate your nerves; the speed and strength of the nerve signal is measured . You may need a lumbar puncture to test a clear, colourless fluid that surrounds and supports the brain and spinal cord . Poor recognition of common peroneal neuropathy without foot drop or the presence of foot drop with normal electrodiagnostic studies thus often results in delayed or no surgical treatment. Our cases document 2 patients presenting with complete foot drop who had immediate resolution after decompression.
Neurologists usually perform an EMG test right after a nerve conduction study. During the nerve conduction study, a provider will put electrodes (stickers) on the surface of your skin. They’ll then deliver a small electrical impulse that will feel like a shock to nerves and record the response. In most cases, they’ll test several different .A related test, the nerve conduction study (NCS), is often performed alongside an EMG. . (compression of the L5 spinal nerve at the L5-S1 spinal segment) and peroneal neuropathy (compression of the peroneal nerve near the knee) can both cause foot drop. NCS is typically normal in radiculopathies and shows abnormal neural activity in other .
Diseases affecting the connection between the nerve and the muscle, such as myasthenia gravis; Disorders of nerves outside the spinal cord (peripheral nerves), such as carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathies; Disorders that affect the motor neurons in the brain or spinal cord, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or polio compression of lower lumbar nerve roots (L4-S1) . Babinski's test. positive findings suggest upper motor neuron lesion. ankle clonus test. associated with upper motor neuron lesion. bulbocavernosus reflex. tests for the presence of spinal shock. . Foot drop. Common peroneal nerve palsy or sciatic nerve compression. Lateral knee compression.
The peroneal nerve, or the fibular nerve, is a significant nerve innervating the lower extremity. With fibers originating from the posterior divisions of L4–S2, the peroneal and tibial nerves are the primary branches of the sciatic nerve, which bifurcates into the tibial and common peroneal nerves proximal to the popliteal fossa in the distal posterior thigh. The .
For example, the peroneal nerve in the lower left leg might show conduction results that are clearly consistent with axonal CMT, yet the median nerve in the right forearm might show normal conduction, especially if it’s early in the disease course. For these reasons, it’s imperative to test nerves in both arms and both legs.
The common peroneal nerve branches from the sciatic nerve and provides sensation to the front and sides of the legs and to the top of the feet. This nerve also controls the muscles in the leg that lift the ankle and toes upward. Injuries .
Lumbosacral radiculopathy is a pathological disorder affecting the nerve root in the lumbosacral region of the spinal cord. Radiculopathy is commonly the result of nerve root compression from a structural lesion (ie, . Nerve conduction study. An NCS detects damage to nerves the way an EMG tests muscle function. During the test, the technician puts electrode patches on your skin over the nerve that may be causing . A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical test used to assess the health and functioning of the peripheral nervous system, which includes the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It is a diagnostic procedure that helps in evaluating nerve damage, detecting nerve-related disorders, and determining the extent and location of nerve injuries . A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test is used to assess nerve damage and dysfunction. Also known as a nerve conduction study, the procedure measures how quickly electrical signals move through .
hardness test standard method
Even though I have had two EMG tests that were normal, I have definite neuropathy symptoms. I feel like I am walking on pepples, my legs tingle constantly. My hands and feet get hot, bright red and painful in the evening, along with painful long lasting foot cramps. I have had nerve pain in my cheek and am constantly constipated. A common sign of a peroneal nerve injury is development of a foot drop. A foot drop is a distinctive way of walking. It occurs when you can’t flex your ankle to take a step forward. Instead, you may lift one knee higher than the other to raise your foot off the ground. Other peroneal nerve injury symptoms include: Inability to move your foot.
The nerve-conduction test is only sensitive to damage in the large-fiber nerves. and does not detect abnormalities in the smallest-caliber nerves. At Johns Hopkins we obtain skin biopsies when patients with symptoms of small-fiber neuropathy have normal nerve-conduction tests.
Lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis may be helpful in the diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy. . Normal nerve conduction studies .Another common cause of foot drop is Lumbar radiculopathy. L5 radiculopathy is the most common lumbar radiculopathy and results from lumbar disc herniation or spondylitis in the spine. . When testing the foot and ankle a positive test for foot drop is NO active dorsiflexion in a non weight bearing position. . Electromyography (EMG) / Nerve .Foot drop is a common and distressing problem that can lead to falls and injury. Although the most frequent cause is a (common) peroneal neuropathy at the neck of the fibula, other causes include anterior horn cell disease, lumbar plexopathies, L5 radiculopathy and partial sciatic neuropathy. And even when the nerve lesion is clearly at the fibular neck there are a variety of .
painful nerve conduction study
These muscles control the swinging of the foot during walking and control plantarflexion on heel strikes. Foot drop can occur due to conditions including muscular, neurologic, spinal, autoimmune, and musculoskeletal disorders. Depending on the etiology, treatment options differ. 1. Anatomy. Lumbar Nerve Roots; There are 5 lumbar vertebrae.The most common causes are peroneal nerve injury and lumbar radiculopathy. It’s treatable in most, but not all, cases. Advertisement. . Several things can damage your common peroneal nerve and cause foot drop. Often, peroneal nerve injuries develop because of a traumatic injury to your knee, leg or ankle. . Nerve conduction tests to .
hardness test standards
hardness test standards pdf
Resultado da FAP
lumbar foot drop but normal nerve conduction test|sensory nerve conduction test